Medicare
Medicare is a federal health insurance program that primarily provides health insurance for Americans aged 65 and older. Establish in 1965, the program expanded in 1972 to cover younger Americans who have a long term disability. Medicare consists of four different parts: Part A covers inpatient hospital stays, Part B covers physician visits, outpatient services and preventative care, Part C covers the Medicare Advantage program, and Part 4 covers outpatient prescription drugs through contracted plans. Medicare reimbursement rates often play a role in the reimbursement rates that private healthcare plans offer.
The Center for Medicare and Medicaid Innovation consistently works with policymakers, providers and other key stakeholders to construct and test alternative payment and delivery models. Medicare has tested a variety of new models, most of which focus on shifting the emphasis to quality care and provide incentives for hospitals and providers to lower spending and decrease cost to patients, while providing higher quality care.
Resources

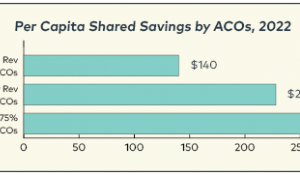
Medicare Spending after 3 Years of the Medicare Shared Savings Program | September 2018
- 1 of 6
- next ›
Related Content
Pages
Pages
Associated Stakeholders:
Secondary menu
Copyright © 2024 Primary Care Collaborative